Breadcrumb

Sexual violence and famine stalk Sudan’s displaced
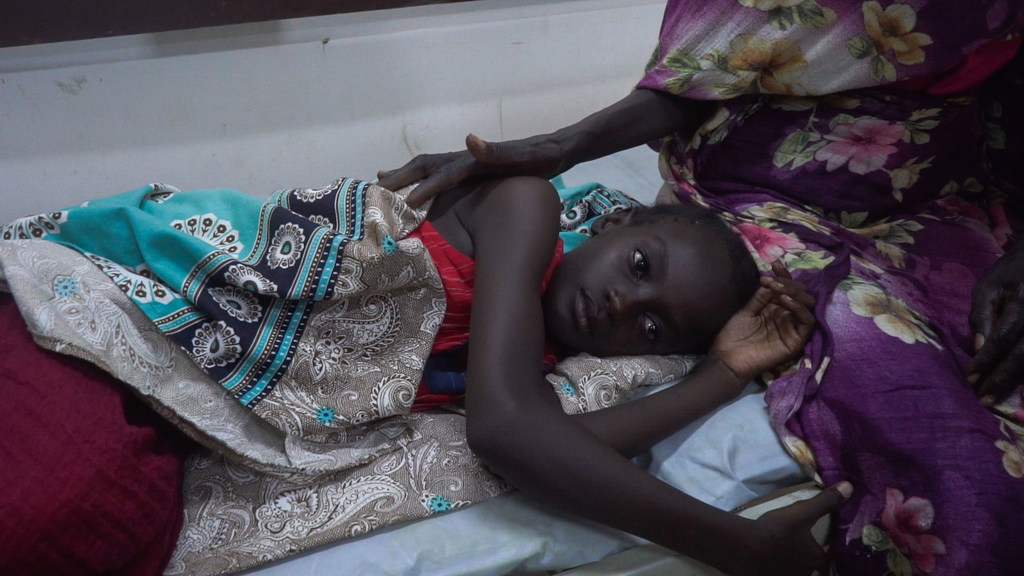
Speaking from Sudan, UN Children’s Fund (UNICEF) spokesperson James Elder described meeting a senior medical worker at a hospital outside Khartoum who had “direct contact with hundreds, hundreds of women and girls, some as young as eight years old, who have been raped. Many have been held captive for weeks on end.”
The medic from Al Nao hospital in Omdurman also spoke “of the distressing number of babies born – born after rape - who are being abandoned now”, the UNICEF spokesperson continued, during an update to journalists in Geneva via videolink from the wartorn country.
Countless horrors
He maintained that “countless atrocities” upon children had gone unreported, often as a result of very limited access.
He also warned that without action, tens of thousands of Sudanese children may die over the coming months, “and that is by no means a worst-case scenario…if there is a measles outbreak, if there is diarrhoea, or if there are respiratory infections, then the terrifying outlook for children in Sudan dramatically worsens.
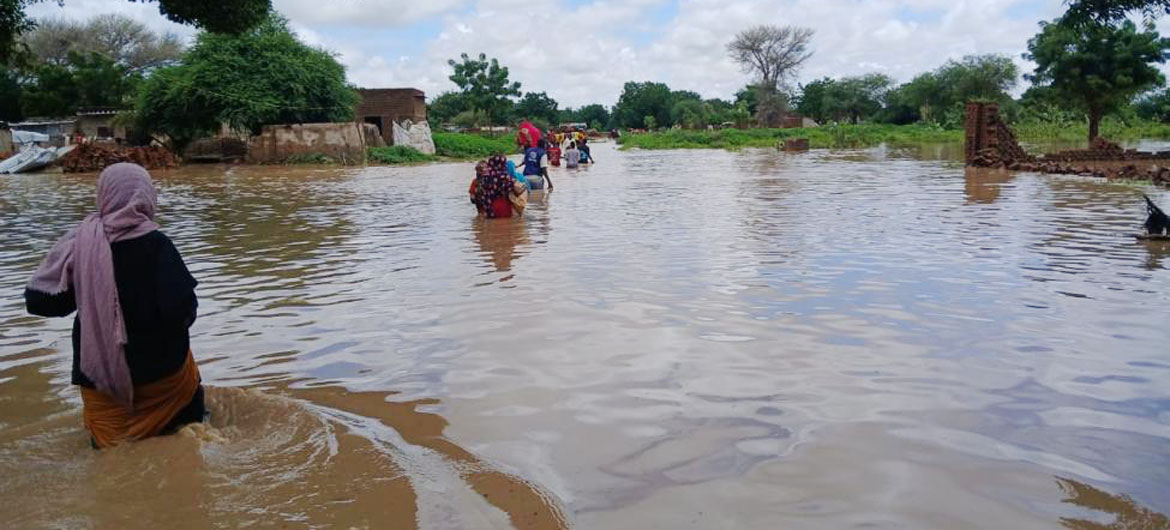
“In the current living conditions, with the heavy rains and the flooding, these diseases will spread like wildfire.”
Echoing that grim update, the UN migration agency, IOM, agreed that flooding had added to the daily challenges facing millions of people whose lives have been uprooted by a battle for control of the country by rival militaries beginning in April 2022, stemming from the overthrow of long-time President Omar al-Bashir in 2019.
Famine fears realized
At the start of the month, global food security experts at the Integrated Food Security Phase Classification (IPC) Famine Review Committee (FRC) reported famine conditions in parts of North Darfur including Zamzam camp near Al Fasher town.
The camp is home to half a million displaced people confronted by extreme food scarcity, which has fuelled malnutrition and death. An additional 13 areas are on the brink of famine.
“The scale of devastation brought by the escalating violence in El Fasher town is profound and harrowing,” the IPC report’s authors noted, amid “persistent, intense and widespread clashes [that] have forced many residents to seek refuge in IDP camps, where they face a stark reality: basic services are scant or absent, compounding the hardship of displacement.”
According to IOM, almost all internally displaced persons across Sudan - 97 per cent - are in localities with acute levels of food insecurity or worse.

Staggering displacement
Worryingly, latest data from the UN agency shows that displacement continues to soar, with more than 10.7 million people seeking safety within the country and many displaced twice or more. Fighting in Sennar state alone displaced over 700,000 people last month with 63 per cent of this number originally displaced from other states, the majority from Khartoum.
Speaking from Port Sudan via video to journalists in Geneva, IOM’s Chief of Mission in the country, Mohamed Refaat, said that more the one in three of Sudan’s internally displaced have come from Khartoum. “That's almost the whole capital of the country has been displaced, so imagine the scale of displacement,” he said.
Citing ongoing aid access obstacles which have prevented UN humanitarians and partners from reaching some of the most vulnerable civilians in Sudan, the IOM officer said that a large number of civilians remain “trapped” in a “very hostile war environment” and with no access to health care services. Many have had to walk large distances in a bid to secure food amid “skyrocketing” prices. “There is a shortage in everything,” Mr. Refaat explained, highlighting how “militias” had also seized control of various locations, restricting the movement of non-combatants.
